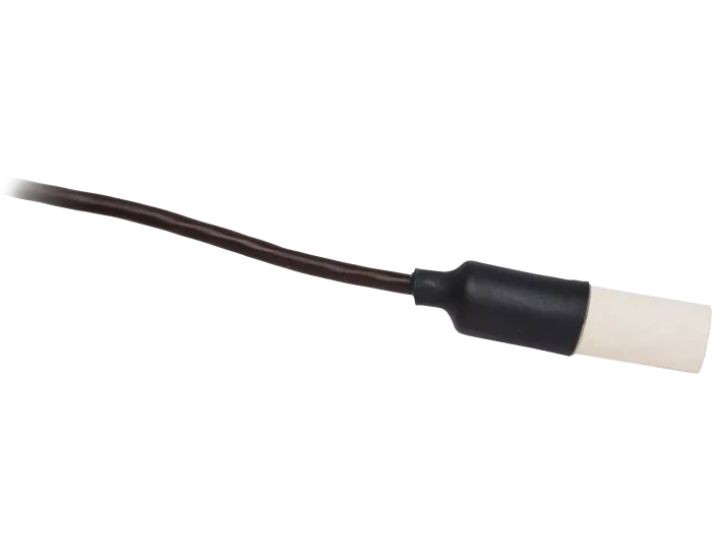
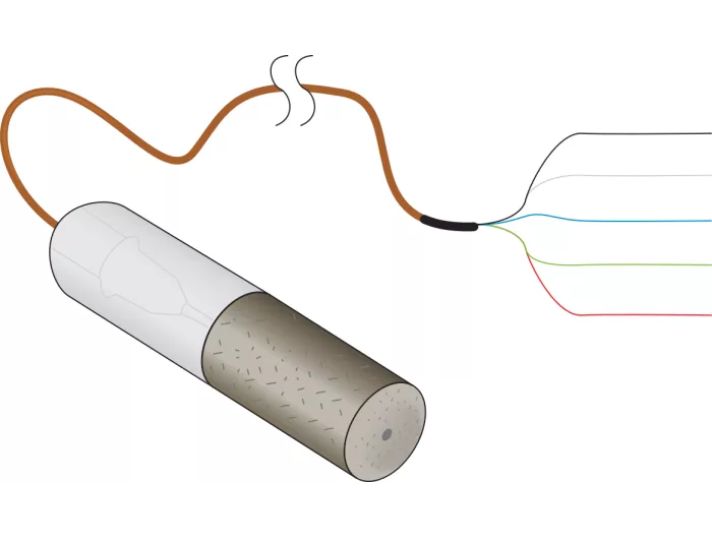
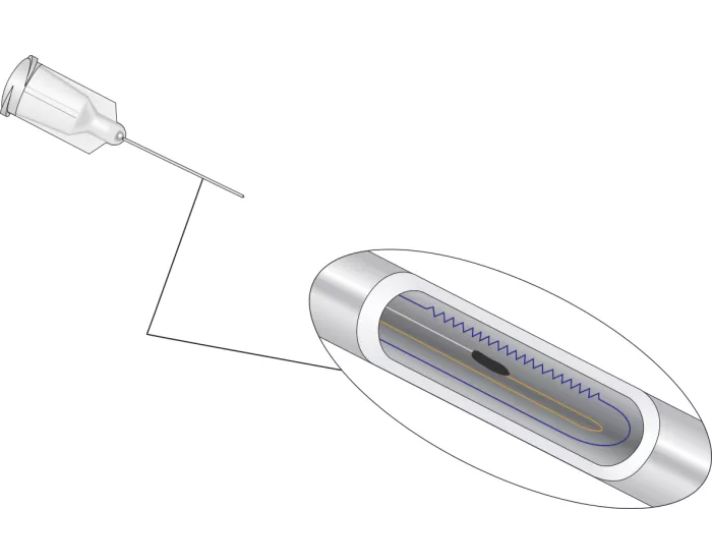
The 229 Water Matric Potential Sensor consists of a heating element and thermocouple placed in epoxy in a hypodermic needle, which is encased in a porous ceramic matrix.
To calculate soil water matric potential, a CE4 or CE8 current excitation module applies a 50 mA current to the 229’s heating element, and the 229’s thermocouple measures the temperature rise. The magnitude of the temperature rise varies according to the amount of water in the porous ceramic matrix, which changes as the surrounding soil wets and dries. Soil water matric potential is determined by applying a second-order polynomial equation to the temperature rise. Users must individually calibrate each of their 229 sensors in the soil type in which the sensors will reside.
A reference temperature measurement is required for the 229’s thermocouple measurement. Options for measuring the reference temperature include:
-
- Thermistor built into the CR6, CR800, CR850, CR1000, CR3000, or CR5000 wiring panel
- PRT built into the wiring panel of the CR9050 or CR9051E input module for the CR9000X Measurement and Control System
Benefits and Features
-
- Compatible with most Campbell Scientific data loggers
- Measures a wide range of matric potential
- Measurements not affected by salts in the soil
- Long lasting, with no maintenance required
- Compatible with AM16/32-series multiplexers, allowing measurement of multiple sensors










Review 229-L Heat Dissipation Matric Potential Sensor
There are no reviews yet.