Measuring rainfall not only helps us better understand climate and weather but also plays a significant role in various fields such as agriculture, water resource management, and environmental protection. In the following article, Reeco will guide you on how to accurately measure rainfall using specialized equipment.
The importance of rainfall measurement
Rainfall measurement is not only essential for environmental management but also plays a decisive role in weather forecasting and preventing risks associated with heavy rainfall and floods. Specifically:

Measuring rainfall for water resource management
Rainfall is the primary source of water for rivers, lakes, and groundwater. Measuring rainfall helps assess water supply and supports the effective management and use of water resources. Rainfall data also assists in forecasting and responding to droughts and floods.
Natural environment management
Rainfall affects the ecosystem and biodiversity of an area. Measuring rainfall helps monitor changes in the natural environment and develop environmental protection measures, especially in forest, land, and floodplain management.
Weather forecasting and disaster prevention
Rainfall data is a crucial component in developing weather and flood forecasting models. Accurate rainfall measurement improves the accuracy of weather forecasts and provides timely warnings of natural disasters such as floods, landslides, and wildfire risks.

Supporting scientific research
Rainfall data is widely used in studies on climate change, the impacts of natural and environmental disasters on human life and ecosystems.
Methods and equipment for measuring rainfall
Currently, there are three common methods for measuring rainfall: recording rain gauges, automatic rain gauges, and simple rain gauges. The specific measurement methods for each of these methods are as follows:

Simple Rain Gauge
Measurement principle: Direct manual measurement using two main tools: a rain gauge bucket and a measuring cylinder.
-
- Rain gauge bucket: Made of metal, with two compartments connected by a conical funnel to reduce evaporation. Area: 200 cm², height: 40 cm, and the bucket’s mouth is 1.5 m above the ground. The rain gauge should be placed at a height 3-4 times the height of obstacles and away from buildings and trees.
- Measuring cylinder: There are two common types of measuring cylinders: P200 and P500. Made of glass, with a mouth area of 10 cm² and a height of 20 cm. Each cylinder is marked with 100 small divisions, each division corresponding to a volume of 2 cm³ (~0.1 mm of water depth in the rain gauge bucket).
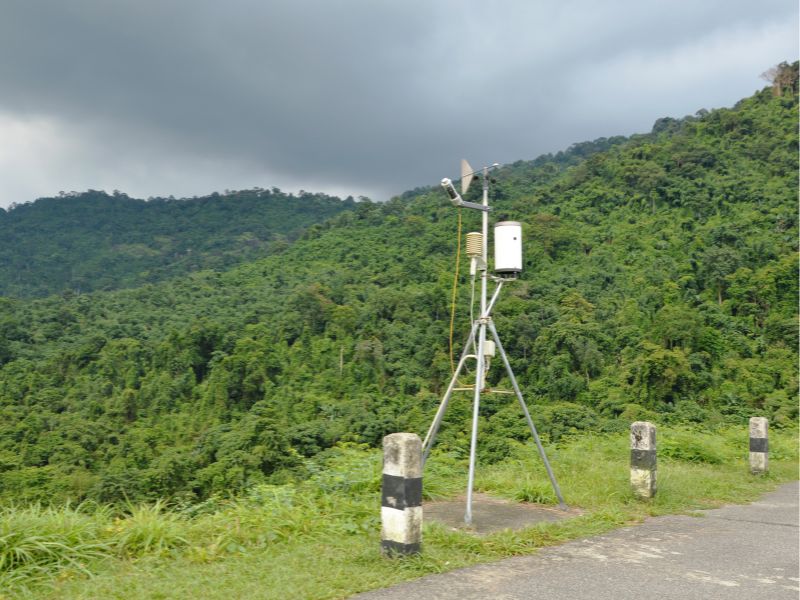
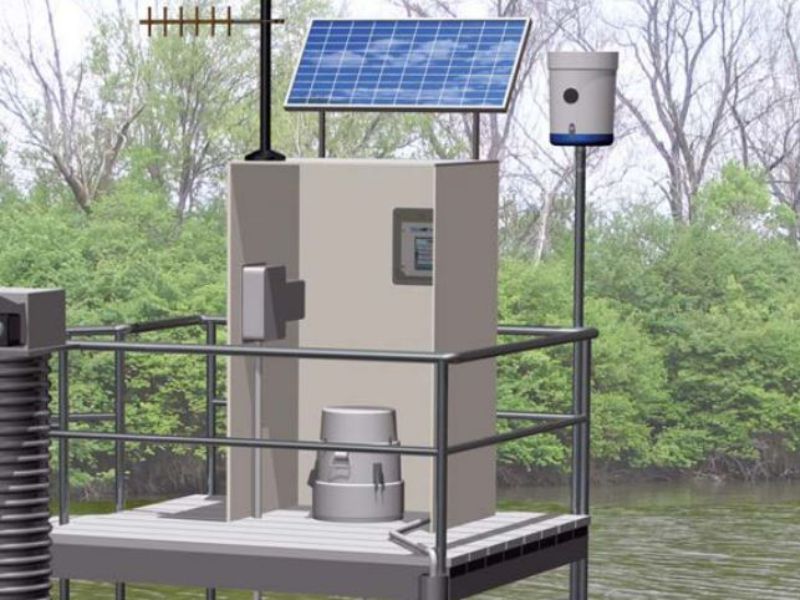
Automatic Rain Gauge
Operating principle: Automatically tips and records rainfall on an electronic device (measured in conjunction with other meteorological factors such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and wind speed). The device automatically records rainfall, stores it in memory, and rainfall data is retrieved using special software.

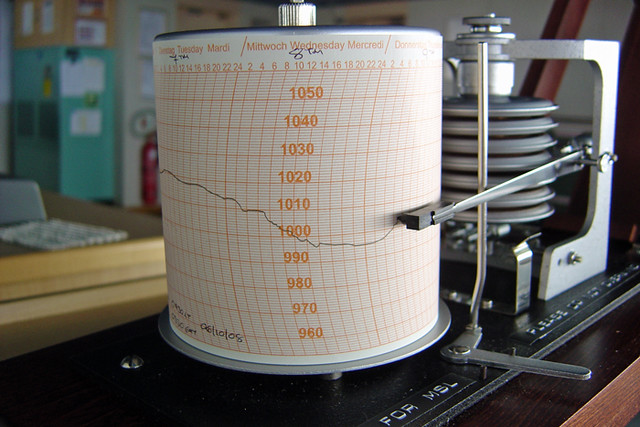
Recording Rain Gauge
Operating Principle: It uses a tipping mechanism to create magnetic induction and then records the amount of rainfall on a diagram to determine the precise rainfall measurement.
Introduction to Common Rain Gauging Devices
If you want to measure rainfall, consider the following high-quality devices:
Rain Gauge
This is the most traditional and common method for measuring rainfall. A rain gauge typically has a cylindrical shape. Rainwater collects in the gauge and fills the marked lines, allowing you to determine the amount of rainfall by measuring the water level in the gauge.

Automatic Rainfall Sensor
This is a modern and automated method for measuring rainfall. Automatic rain sensors are typically placed in strategic locations and use electronic sensors to automatically record rainfall, then transmit the data to an environmental management center or weather forecasting station.
Rainfall Meter
A rainfall meter is a device used for accurately measuring rainfall. It typically has the shape of a box or a cylinder, and its surface is designed to collect and measure rainwater as it falls.
As rain falls, it flows into the surface of the rainfall meter and collects in an internal reservoir. The surface of the meter often has graduated markings to help measure the height of the rainwater in the reservoir. Based on this height, users can determine the amount of rainfall that has occurred over a specified period.
Features of rain measurement devices
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|